Before going into the details of Analog and Digital Circuits, let us take a quick look at Electronics, typical electronic system and different types of signals.
Introduction
Electronics, as a major sub branch of Electrical Engineering, has been an important part of engineering world as well as a normal human being from the mid twentieth century. As a branch of electrical engineering, electronics deals with flow of current, but this current flow is due to a controlled flow of electrons (or charge carriers, to be generic) in gas or vacuum in early stages to solid state semiconductors in modern devices. In fact, the major breakthrough in the field of electronics is the use of Semiconductor materials, which made electronic circuits and devices small, cheap, reliable and consume very low power.
Typical Electronic System
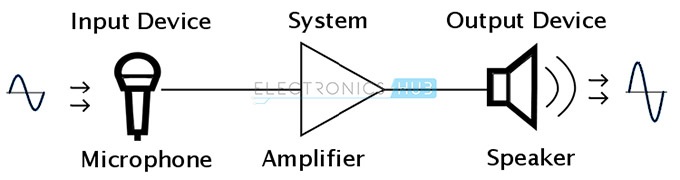
A majority of applications of electronics are in the field of communication. So, let us take and example of a simple communication system and see what a typical electronics system looks like. The system of discussion is the Public Addressing System. If the speaker wants to address a large set of audience like in an auditorium or a concert stadium, he (or she) speaks in front of a device called Microphone or simply Mic.
Microphone is a device that converts sound waves from the speaker into electrical signals. But the energy (or the amplitude) of the electrical signals from the microphone is very small. If we send this small amplitude signal over large distances, it loses its strength due to various losses and cannot drive the loud speaker. So, before transmitting the electrical signals from the microphone to the loudspeaker, they must be amplified in amplitude. An Amplifier is an electronic system or device, which takes in a small electrical signal and boasts its amplitude by a huge margin and produces a high amplitude electrical signal. The amplified signal can now be fed to loudspeakers in order to drive them.
Representation of Signals
The main motivation of designing and building an Electronic Circuit or a System is to process information or energy. Amplifier, Radios, Computers etc. are examples of typical electronic systems which process the information as seen in the previous Public Address System example. In general, processing information includes the following functions:
Information Translation Information Storage Information Manipulation or Computation
The other purpose of electronic system is to process power as in case of the complex power supplies or the simple light bulb. Irrespective of the purpose i.e. to process information or energy, these physical quantities are represented as signals or electrical signals in an electronic circuit, to be specific. These electrical signals can be either current or voltage and a network of electronic circuit will process these signals.
Analog Signals and Digital Signals
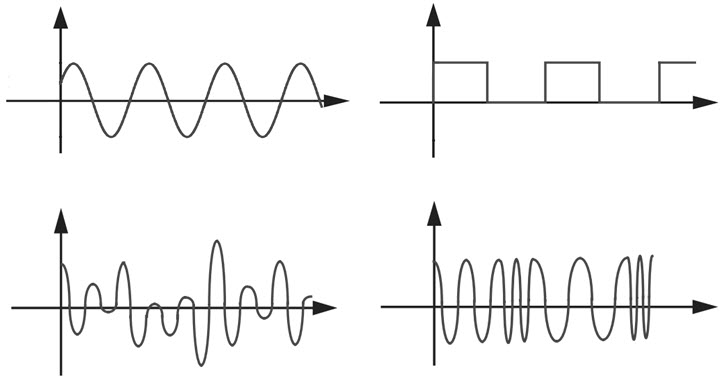
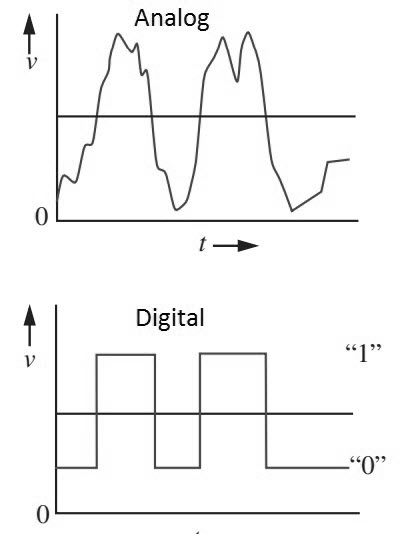
Almost all the signals in the World are analog i.e. they are continuously varying values. There are lot of continuously variable signals or simply analog signals in nature like light, motion, sound, temperature, pressure etc. The following image shows a typical analog signals.
Digital Signals vary in discrete levels, in contrast to the continuous representation of analog signals. Generally, the discrete levels in a digital signal are just two values: ON and OFF. Even though all the physical signals of the nature are continuous analog signals, representing signals as discrete values has its own advantages.
Traditionally and historically, all electronic devices processed analog information only. But the developments in technology has led to using digital signals for easy processing and such techniques are called Digital Signal Processing.
Classification of Electronic Circuits and Systems
Signal Processing can be implemented using a variety of semiconductor electronic devices like PN Junction Diodes, Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT), Field Effect Transistors (FET) etc. in combination with passive components like resistors and capacitors. The interconnection of many such circuits, where each circuit performs a specific task, results in a complete Electronic System or device. The design of electronic circuits can be undertaken in two ways based on the above understanding of Analog and Digital Signals. They are:
Analog Circuits Digital Circuits
Analog Circuits and Digital Circuits is a classic way of differentiating between two types of electronic circuits based on the signals they process. To put it in simple words, Analog Circuits deals with continuous analog signals whereas Digital Circuits deals with discrete digital signals. Now, let us see each of these types with simple examples.
Analog Circuits
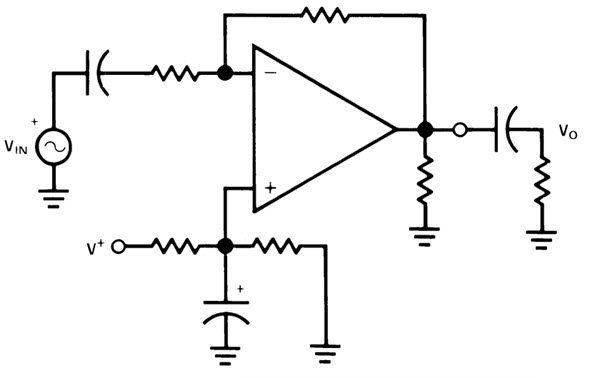
As mentioned earlier, an Analog Circuit is a type of Electronic Circuit which processes analog data using analog components like resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors etc. Analog Circuits can be quite simple like a combination of resistors to form a voltage divider or a combination of Op-amps (which internally contain transistors), resistors, diodes etc. to form an amplifier. The following is an example of a simple Analog Circuit.
This is a simple amplifier circuit implemented using Op-amp, resistors and capacitors. By selecting appropriate values for resistors and capacitors, you can achieve a significant gain at the output. Old-school Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO) is an Analog Device that can detect ad analyse analog signals.
Digital Circuits
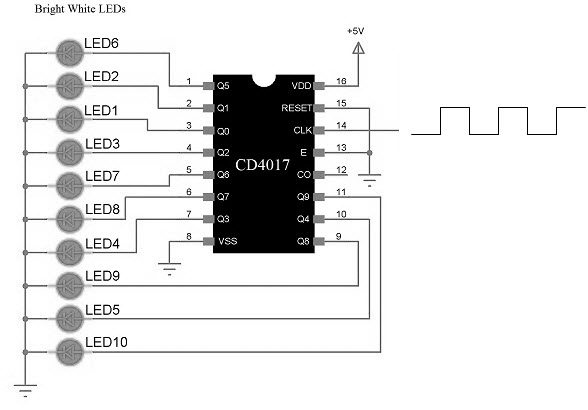
On the contrary, a Digital Circuit is also a type of an electronic circuit that is predominantly built using Digital electronic components to process digital signals. At low level, the digital circuits consist of a combination of transistors, logic gates (AND, NAND, NOT etc.) and at high level, microcontrollers and processors. All Digital circuits work on the binary digital signalling i.e. using only two voltage levels to represent the status signal i.e. ON or OFF. For performing various digital signal processing, all digital circuits incorporate fast switching devices like diodes and transistors and some of the important functions of digital circuits are multiplexing, demultiplexing, memory, combinational logic, sequential logic, etc. The following is an example of a simple digital circuit built using CD4017 Counter IC.
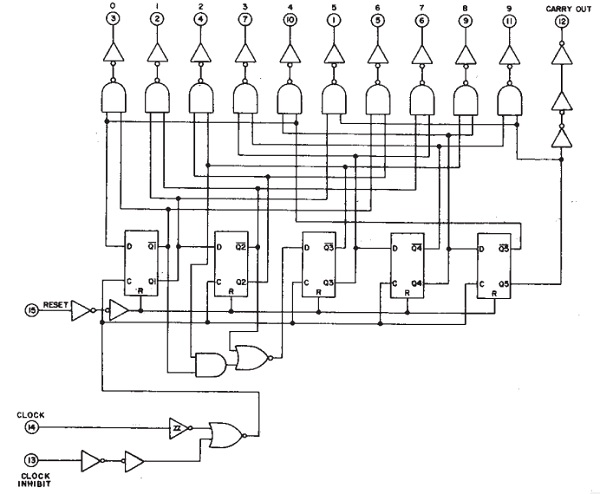
This might not be clear but if you take a look at the internal structure of the CD4017 IC, you will see that it is essentially constructed using AND Gates, NOR Gates, Inverters, Flip-flops and buffers.
All the modern computers work in digital realm even though they are built using analog electronic components. Since most of the physical world is analog, the analog signals must be converted to digital signals before the computers can perform any operations.
Differences between Analog Circuits and Digital Circuits
At this point, the differences between Analog Circuits and Digital Circuits might be clear but as an aid for easy understanding, we have tabulated the differences.
Analog Circuits Digital Circuits Analog circuits operate on continuously variable signals also known as Analog Signals. Digital Circuits operate on discretely variable signals or Digital signals i.e. the signal exists only in two levels: 0 and 1 (binary digital signalling). Depending the efficiency and precision, it is quite difficult to design Analog Circuits. Digital Circuits are relatively easy to design with many automated tools available for various stages of design and analysis. When interacting with the physical world, analog circuits can directly accept the signals from outside as the data is already analog. If a digital circuit has to acquire data from physical world, the analog signals must be converted to digital signals first. As there is no need for data conversion, there is ideally no loss of information. During the process of converting analog signals to digital signals, there might a significant amount of data loss, which can result in loss of information. If precision and accuracy are not a criterion, then analog circuits can be simple and inexpensive. Even with simple design techniques and at low cost, the digital circuits can provide good accuracy and precision. Due to the lack of skilled engineers and the complexity of the designs, analog circuits can turnout to be quite expensive. Advanced Integrated Circuits technologies and many other factors help the digital circuits to be reliable, lower in cost and smaller in size.
Comment *
Name *
Email *
Website
Δ





![]()