In simple terms, when you open any website, the browser stores a piece of static information (HTML, CSS, Logo’s, etc) about the site in form of Cache, so next time when you open the page, it directly requests the data from cache for quick loading reducing the site loading time.
What is Cache in Google Drive?
Now there are two types of Cache build-up based on the usage, one on the browser and the second on the mobile app. Let us look at both the cache stores.
Google Drive Cache in Browser
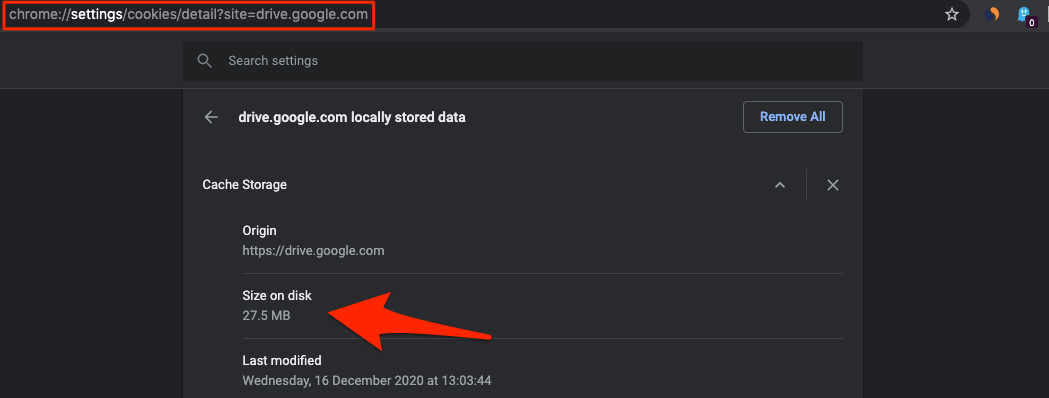
When you open Google Drive in your Browser. The browser stores some static information related to the site, this may include but not limited to logos, document cache, HTML, CSS, and other data that generally do not change very often. This static container is Cache of Google Drive. You can check the disk space taken up by the cache for GDrive in Chrome Browser using the following URL code.
The stored cache will help the browser to quickly load the website when requested. It also helps load any documents on a fully loaded website even when the internet is suddenly disconnected.
Google Drive Cache in Mobile
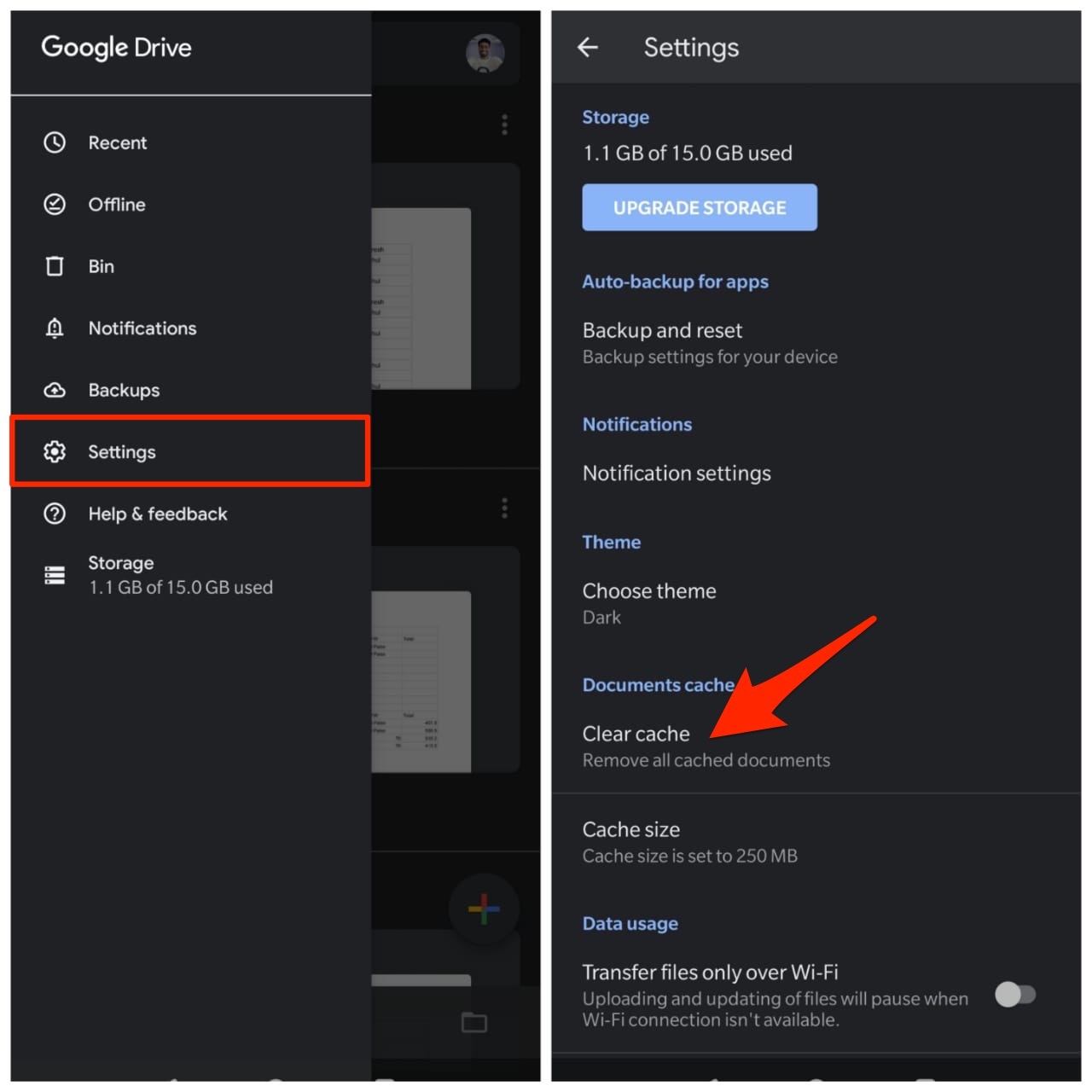
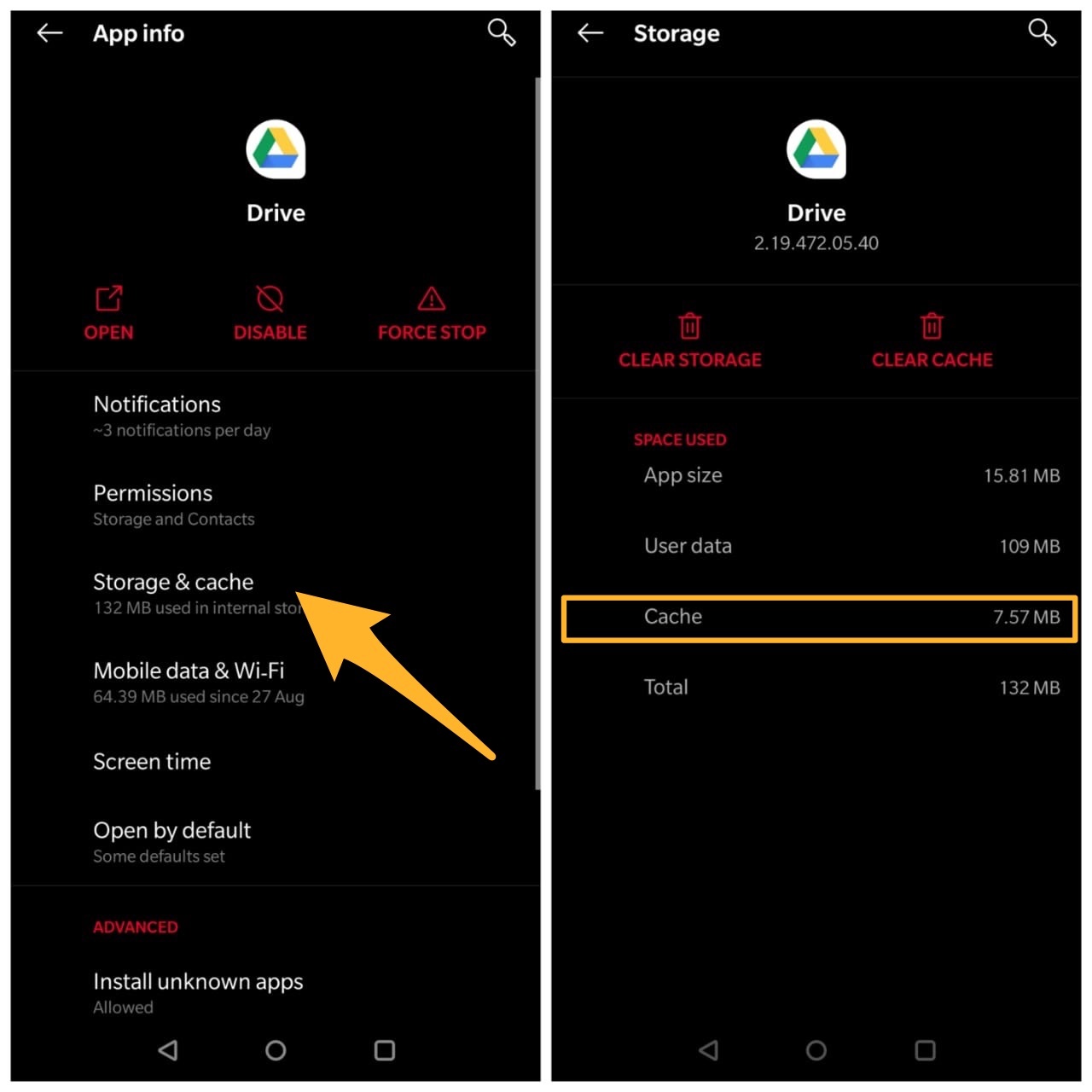
The mobile app for Google Drive also builds cache, the app itself builds the Document Cache and the system develops the app cache. The Document Cache helps in loading the Google Docs stored in the drive quickly, it also helps the app to work offline to open some specific doc files.
The app offers an option to even increase the cache size up to 1GB. You can even delete the cache in case your device is low in storage space. The android and iOS systems also store the cache, but it is generally the application cache and has nothing to do with the content. The mobile cache works similar to the cache in Google Drive for the browser. The app cache stores the assets of the app so that when you open the app it loads quickly with all the necessary details.
So, with that being said. The Cache for Google Drive is an important component, it reduced load time, stores assets, and helps load docs offline.